Date
May 12, 2020
Tags
url
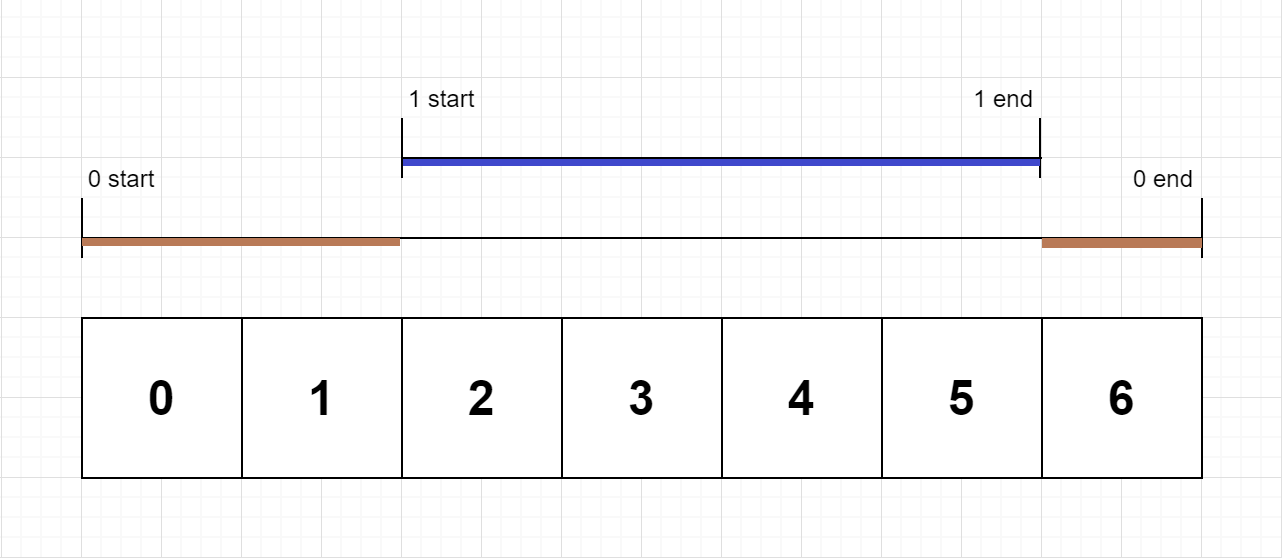
On a single threaded CPU, we execute some functions. Each function has a unique id between 0 and N-1.We store logs in timestamp order that describe when a function is entered or exited.Each log is a string with this format: "{function_id}:{"start" | "end"}:{timestamp}". For example, "0:start:3" means the function with id 0 started at the beginning of timestamp 3. "1:end:2" means the function with id 1 ended at the end of timestamp 2.A function's exclusive time is the number of units of time spent in this function. Note that this does not include any recursive calls to child functions.The CPU is single threaded which means that only one function is being executed at a given time unit.Return the exclusive time of each function, sorted by their function id.Example 1:Input:
n = 2
logs = ["0:start:0","1:start:2","1:end:5","0:end:6"]
Output: [3, 4]
Explanation:
Function 0 starts at the beginning of time 0, then it executes 2 units of time and reaches the end of time 1.
Now function 1 starts at the beginning of time 2, executes 4 units of time and ends at time 5.
Function 0 is running again at the beginning of time 6, and also ends at the end of time 6, thus executing for 1 unit of time.
So function 0 spends 2 + 1 = 3 units of total time executing, and function 1 spends 4 units of total time executing.
- log是按照时间顺序,输出是按照序号。这样建立个字典保存信息,然后遍历log,之后再输出即可
提交发现,存在一个方法多次调用的方式。只用key做字典的方式不能存储所有需要信息,会存在覆盖。
- 考虑使用栈结构,每次出现新log时可以得到一个消耗时间
由于'start'和‘end’会影响时间段的计算,所以增加了这部分的处理。还可以优化下不做判断而是在记录last time时处理
